
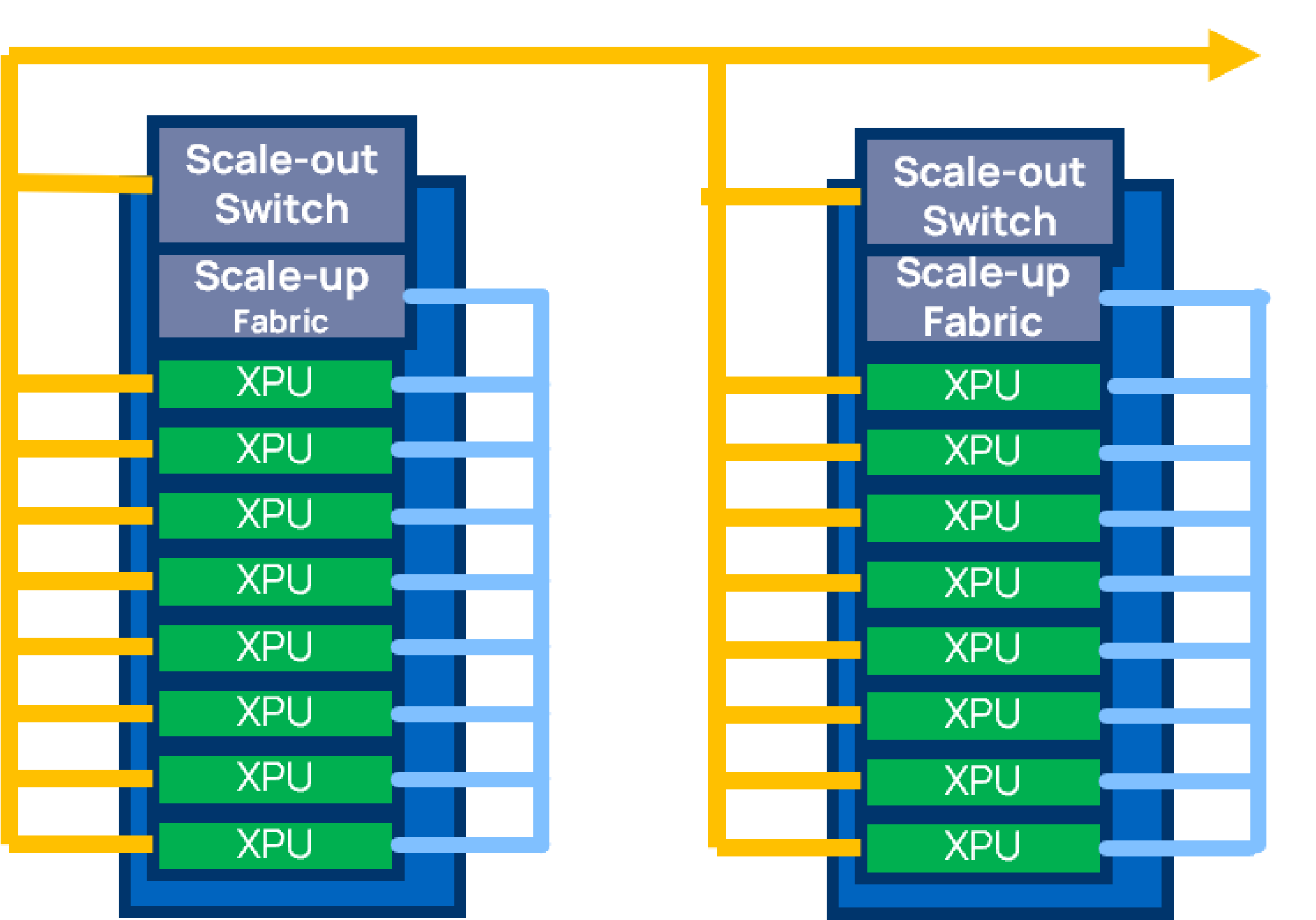
WeaveIP fabric providing non-blocking switching between a large number of ports for the emerging scale-up and scale-out systems
AI, especially GenAI, is driving the need for much greater compute acceleration and data movement for both training and inference. Scale-up (vertical scaling) increases a server’s performance, while scale-out computing (horizontal scaling) increases the number servers to process workloads in parallel. While the industry has focused more on compute, the real challenge now is on the data movement bottleneck.
While scale-out has high growth requirements, scale-up has even more extreme performance demands with larger sets of tightly-coupled compute elements that are latency-sensitive. NVIDIA has turbocharged scale-up with NVLink™ interconnect and NVSwitch™ switching to drive rapid market growth. However, market needs are outstripping projected roadmaps. The arrival of new interconnect standards like Ultra Accelerator Link™ or UALink™ has drawn innovation to this space as well.
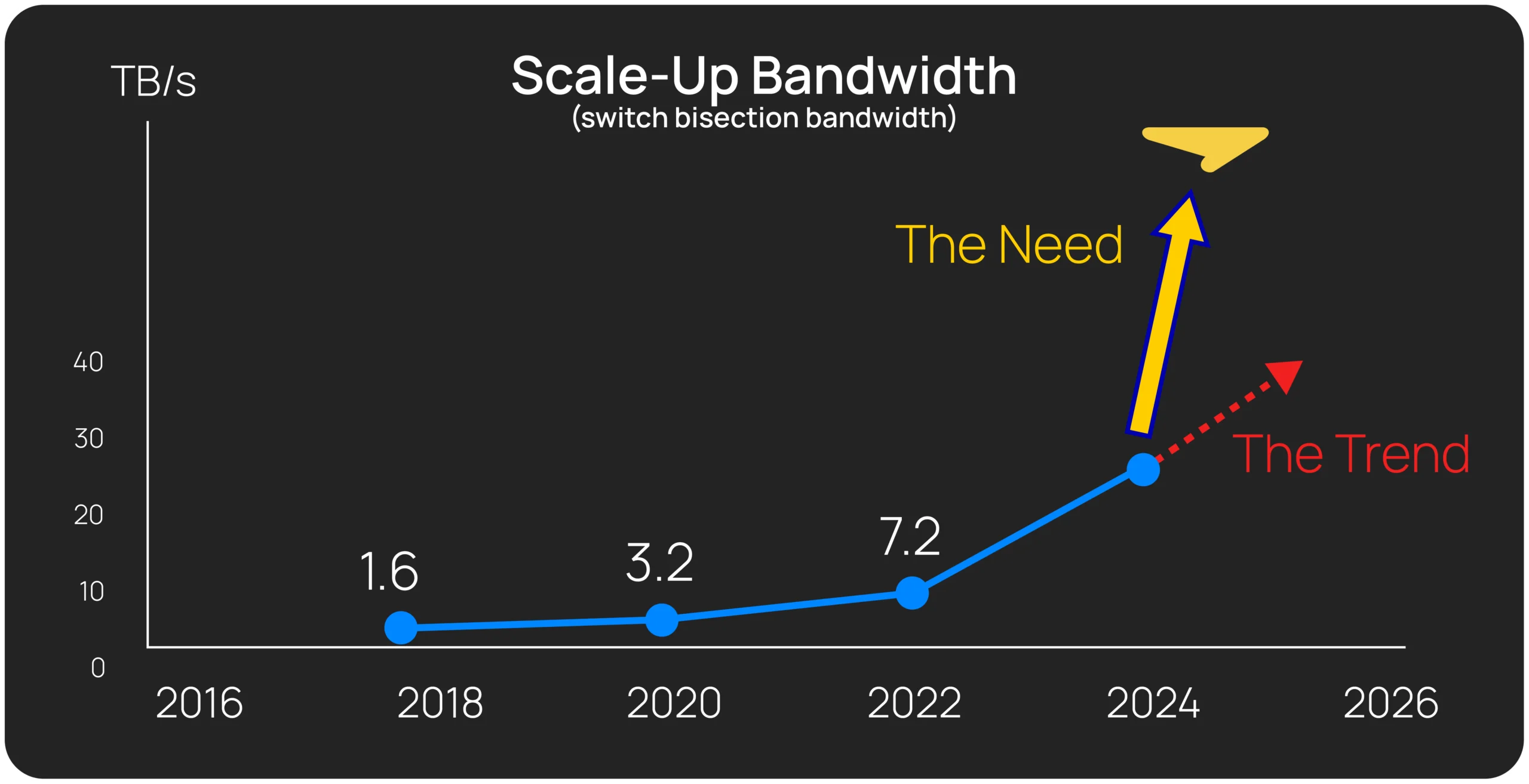
Legacy crossbar-based methods are inadequate to provide this level of scaling for the upcoming generations.

The NeuraScale fabric is highly configurable and delivers the benefits of the non-blocking, crossbar without the downsides of extremely intensive implementation needed for the higher end port counts, along with the inherent limitations that accompany cross bar switches in terms of scaling to high port counts.
NeuraScale’s distributed approach does not compromise latency, in fact maintaining extremely low latency through wide buses and large port count. The flexibility offered in implementation allows easier access to all edges of the chiplet for I/O and PHYs to create larger scale through chiplets.

Like other WeaveIP™ fabrics, the NeuraScale fabric can be analyzed, configured, designed and implemented using the WeaverPro™ FabricStudio™ software platform. This provides the user with very granular control from concept through implementation. It includes post-silicon tuning with a wide range of programmability.